translink bus shelter
This guide provides a detailed overview of TransLink bus shelters, covering their design, features, locations, advertising opportunities, and maintenance. We explore the role these shelters play in public transportation and delve into the behind-the-scenes aspects of their management and upkeep.
Design and Features of TransLink Bus Shelters
Shelter Structure and Materials
TransLink bus shelters are typically constructed from durable, weather-resistant materials designed to withstand various climatic conditions. Common materials include tempered glass, aluminum, and steel, ensuring longevity and safety for passengers. The design often incorporates features like seating, lighting, and information displays, enhancing passenger comfort and accessibility. Specific design elements may vary depending on location and accessibility requirements.
Accessibility Features
Many TransLink bus shelters are built with accessibility in mind. This includes features like ramps for wheelchair users, clear signage, and adequate space for maneuvering. The incorporation of these features ensures that the shelters are inclusive and easily accessible to all members of the community. Compliance with relevant accessibility standards is a key priority in the design and construction process.
Advertising Opportunities
TransLink bus shelters often provide advertising opportunities for businesses. These ads can be displayed on the shelters themselves, offering significant visibility to commuters. Advertising space is typically managed and sold through dedicated advertising companies or directly by TransLink. The specific advertising opportunities and pricing vary and can be found on TransLink’s official advertising partners' websites. For example, some providers might offer both static and digital advertising panels, allowing for dynamic campaigns and targeted reach.
Locations and Distribution of TransLink Bus Shelters
The geographical distribution of TransLink bus shelters is extensive, covering numerous bus routes and key transit hubs. The precise locations of individual shelters can typically be found on TransLink’s official website or mobile application, which often provides real-time bus arrival information and shelter maps. Strategic placement ensures that shelters are conveniently located near bus stops, maximizing passenger convenience and usage.
Maintenance and Upkeep of TransLink Bus Shelters
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and safety of TransLink bus shelters. This involves tasks such as cleaning, repairing any damage, and replacing worn-out components. TransLink typically contracts with specialized maintenance companies to perform these services, guaranteeing that shelters remain in good condition and provide a safe environment for passengers. Reporting damage or maintenance issues can often be done through TransLink's online channels.
The Role of TransLink Bus Shelters in Public Transportation
TransLink bus shelters play a vital role in enhancing the overall public transportation experience. They provide a safe, comfortable, and informative waiting area for commuters, improving passenger satisfaction and promoting the use of public transit. Beyond simply offering shelter from the elements, these structures contribute to the overall aesthetic of the transportation network and its integration into the urban landscape.
Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd. and Smart Bus Shelter Solutions
Companies like Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd. (https://www.luyismart.com/) are at the forefront of designing and manufacturing advanced bus shelter solutions. Their expertise in creating durable, innovative, and accessible shelters contributes to the overall quality of public transit experiences. They often incorporate smart features such as integrated digital displays, USB charging ports, and real-time information systems, significantly improving commuter experience. You can explore their innovative solutions for sustainable and intelligent bus shelter designs on their website.
Comparison of Different TransLink Bus Shelter Designs
| Feature | Standard Shelter | Premium Shelter |
|---|---|---|
| Seating | Basic bench seating | Enhanced seating with backrests |
| Lighting | Standard LED lighting | Improved lighting with motion sensors |
| Information Display | Basic timetable display | Real-time information display and digital screens |
Note: Specific features and designs may vary depending on location and availability. This table presents a generalized comparison.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продукты-
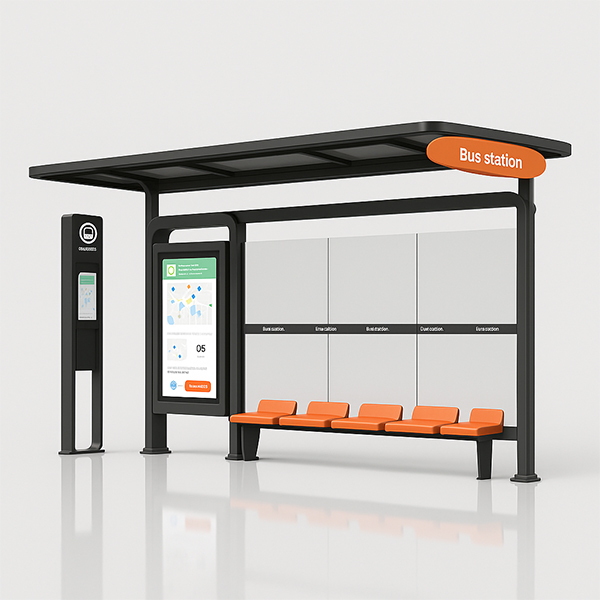 Smart Bus Station
Smart Bus Station -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop -
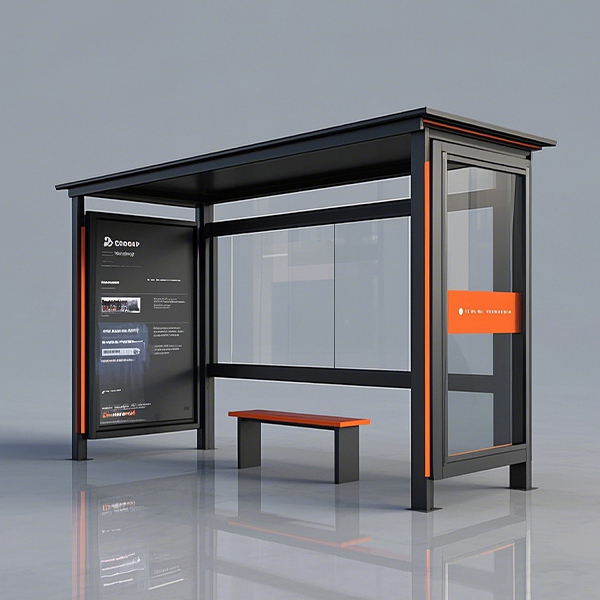 Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter
Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop -
 Rooftop Advertising Bus Stop Shelter
Rooftop Advertising Bus Stop Shelter -
 Bus Stop Shelter
Bus Stop Shelter -
 Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter
Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter -
 Simple Bus Shelter
Simple Bus Shelter -
 Bus Stop Shelter
Bus Stop Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop -
 Glass Roof Bus Shelter
Glass Roof Bus Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop Shelter
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop Shelter