the bus shelter
This guide explores the multifaceted world of the bus shelter, delving into its design, functionality, societal impact, and the innovative technologies transforming this often-overlooked piece of urban infrastructure. We'll examine various shelter types, materials, and the crucial role they play in public transportation and community well-being. Learn about the sustainability considerations, accessibility features, and even the advertising potential associated with the bus shelter.
Types of Bus Shelters
Traditional Bus Shelters
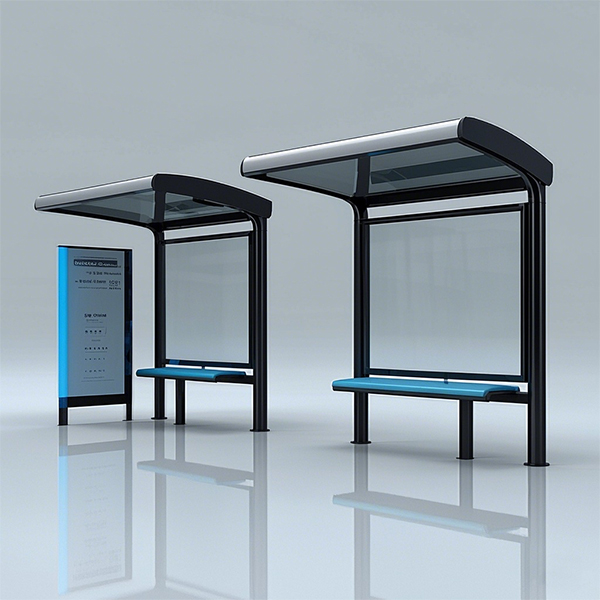
Classic bus shelters often feature a simple, open-sided structure with a roof for protection from the elements. Materials typically include steel, concrete, or wood, with glass or polycarbonate panels for wind protection. These designs prioritize affordability and practicality.
Modern Bus Shelters
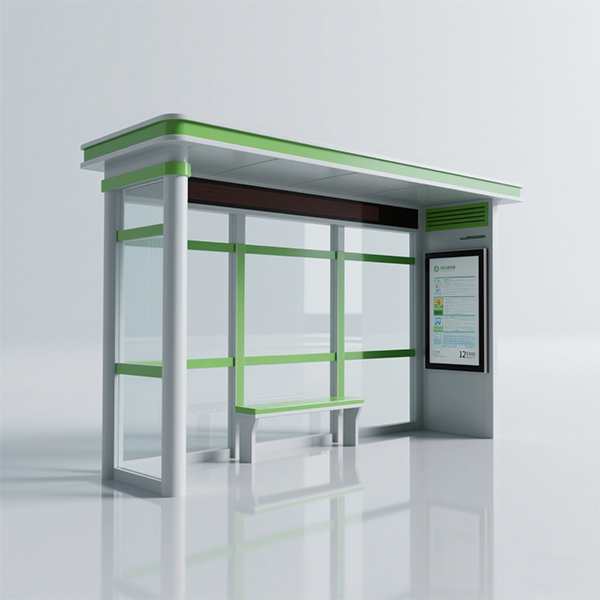
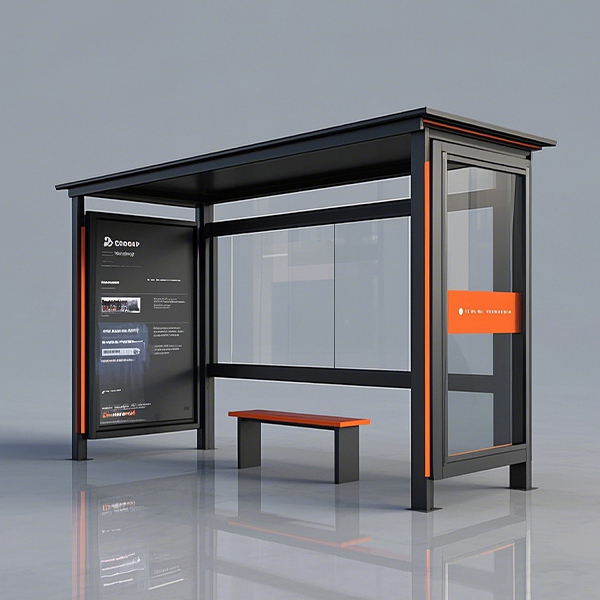
Modern designs incorporate advancements in materials and technology. You’ll find structures built with sustainable materials like recycled plastic or aluminum, offering enhanced durability and aesthetics. Many modern bus shelters integrate features such as solar panels for lighting or USB charging ports.
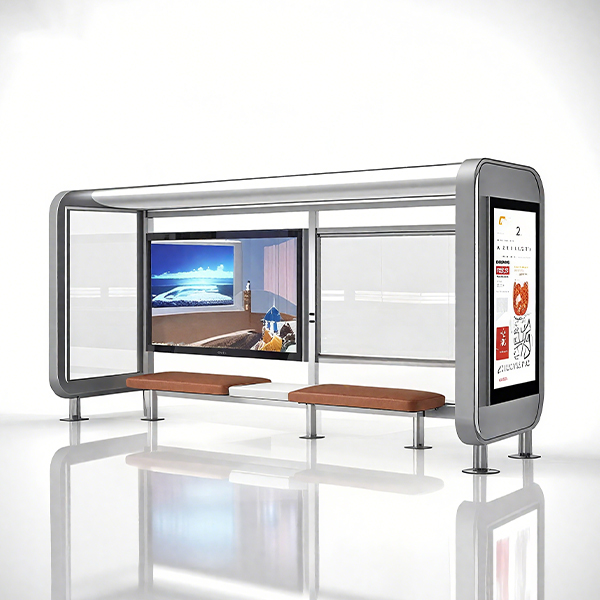
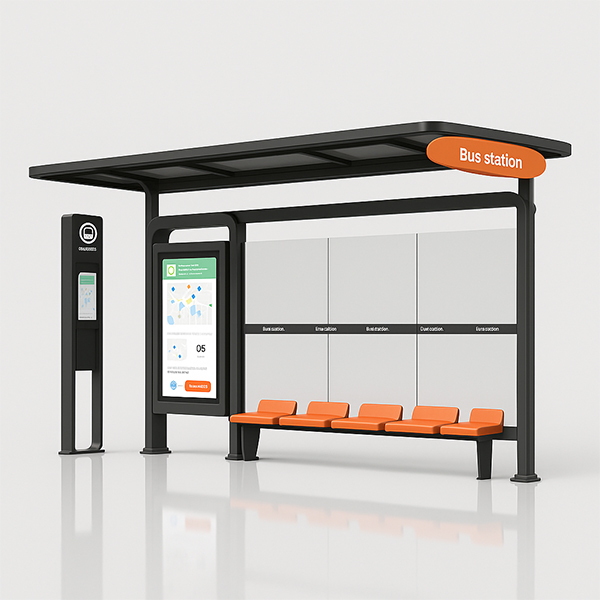
Smart Bus Shelters
Smart bus shelters represent the cutting edge, integrating technology for real-time information displays, Wi-Fi hotspots, and even air quality sensors. These sophisticated shelters enhance passenger experience and contribute to smart city initiatives. Companies like Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd. are at the forefront of developing these advanced solutions for urban areas.
Materials and Construction
The choice of materials significantly impacts the bus shelter's lifespan, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal. Common materials include:
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Strong, durable, relatively inexpensive | Susceptible to rust, may require maintenance |
| Concrete | Durable, weather-resistant | Heavy, expensive to install, less aesthetically pleasing |
| Recycled Plastic | Sustainable, low maintenance, durable | Can be more expensive than traditional materials |
The Role of the Bus Shelter in the Community
The bus shelter serves as more than just a waiting area. It's a vital component of public transportation infrastructure, promoting safety, accessibility, and community well-being. Its presence fosters a sense of security, particularly at night or in less populated areas. Well-designed bus shelters also contribute to a more positive and welcoming public space.
Sustainability and Accessibility in Bus Shelter Design
Modern bus shelter designs increasingly prioritize sustainability and accessibility. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient lighting, and features that cater to individuals with disabilities, such as wheelchair ramps and tactile paving. Sustainable bus shelters can significantly reduce their environmental impact.
The Future of the Bus Shelter
The future of the bus shelter is likely to involve greater integration of technology and a stronger focus on sustainability. Expect to see more smart shelters equipped with advanced features, enhancing passenger experience and contributing to smarter, more sustainable cities. The continued innovation from companies like Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd. will play a significant role in shaping this evolution.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция