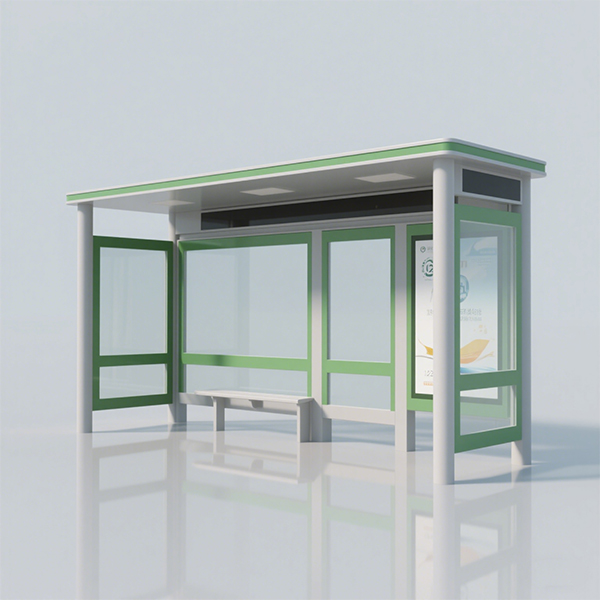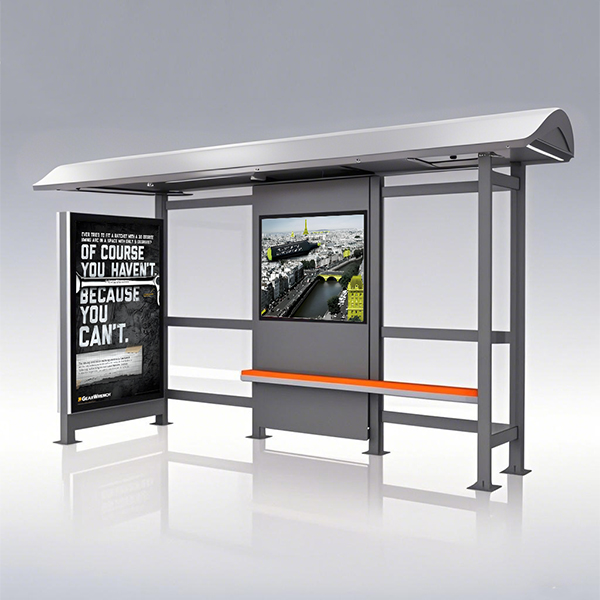
rural bus stop shelter
This comprehensive guide explores the crucial aspects of designing and maintaining effective rural bus stop shelters. We'll cover everything from choosing the right materials and considering accessibility to ensuring long-term durability and passenger comfort. Learn how to create safe and welcoming waiting areas in rural communities.
Understanding the Unique Needs of Rural Bus Stop Shelters
Challenges in Rural Environments
Rural bus stop shelters face unique challenges compared to their urban counterparts. These include factors like extreme weather conditions (intense sun, heavy snow, strong winds), vandalism, limited maintenance budgets, and potentially dispersed populations. Understanding these challenges is critical to designing effective and sustainable shelters.
Prioritizing Durability and Low Maintenance
Given the often-remote locations and limited maintenance resources, prioritizing durable materials and low-maintenance designs is paramount. This means choosing materials resistant to weathering, vandalism, and graffiti. Simple, robust designs are preferable to complex structures that are difficult to repair or maintain.
Key Design Considerations for Rural Bus Stop Shelters
Material Selection for Strength and Weather Resistance
The choice of materials significantly impacts the longevity and effectiveness of a rural bus stop shelter. Consider using materials like treated timber, galvanized steel, or durable composite materials. Each option offers advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal. For example, treated timber offers a natural look, but requires regular maintenance to prevent rot. Galvanized steel is highly durable and resistant to corrosion, but can be more expensive. Composite materials offer a balance between durability and aesthetics, often requiring minimal maintenance.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Designing for accessibility is crucial. Shelters should adhere to accessibility guidelines, ensuring easy access for individuals with disabilities. This includes features like ramps, appropriate seating heights, and clear signage. Consider the needs of elderly passengers and those with mobility impairments.
Shelter Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of the shelter should be appropriate for the expected passenger volume and local conditions. Factors to consider include seating capacity, adequate standing room, and protection from the elements. A well-designed shelter should provide ample space for passengers to wait comfortably without feeling crowded.
Lighting and Security
Adequate lighting is essential for safety and security, particularly in rural areas with limited ambient lighting. Consider energy-efficient LED lighting integrated into the shelter's design. Security features such as robust construction, vandal-resistant materials, and well-lit surroundings can help deter vandalism and create a safer environment.
Maintenance and Long-Term Sustainability
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
Regular inspection and cleaning are crucial for maintaining the longevity and functionality of the rural bus stop shelter. A preventative maintenance schedule can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Regular cleaning helps to prevent the build-up of dirt, grime, and graffiti.
Repair and Replacement Strategies
Developing a clear plan for repairs and replacements is essential to ensure the shelter remains in good condition. This should involve identifying potential points of failure, sourcing replacement parts, and having a process in place for timely repairs. Consider the cost-effectiveness of different repair methods and materials.
Case Study: A Successful Rural Bus Stop Shelter Project
While specific examples are dependent on location and project details, a successful project would involve close collaboration between the community, transportation authorities and the supplier (such as Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd.). This collaboration would ensure that the chosen shelter design meets the unique needs of the rural community while adhering to safety and accessibility standards. The focus would be on selecting durable, low-maintenance materials, implementing effective security measures, and establishing a clear maintenance plan.
Conclusion
Designing and maintaining effective rural bus stop shelters requires careful consideration of several factors. By prioritizing durability, accessibility, and low-maintenance design, communities can create safe, welcoming, and sustainable waiting areas for their passengers. Remember that regular maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of these vital public infrastructure assets.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продукты-
 Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter
Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter -
 Smart Bus Station
Smart Bus Station -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop -
 Curved Shed Bus Shelter
Curved Shed Bus Shelter -
 Double Light Box Bus Shelter
Double Light Box Bus Shelter -
 Bus Stop Shelter
Bus Stop Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter
Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter -
 Glass Roof Bus Shelter
Glass Roof Bus Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop -
 Stainless Steel Bus Shelter
Stainless Steel Bus Shelter