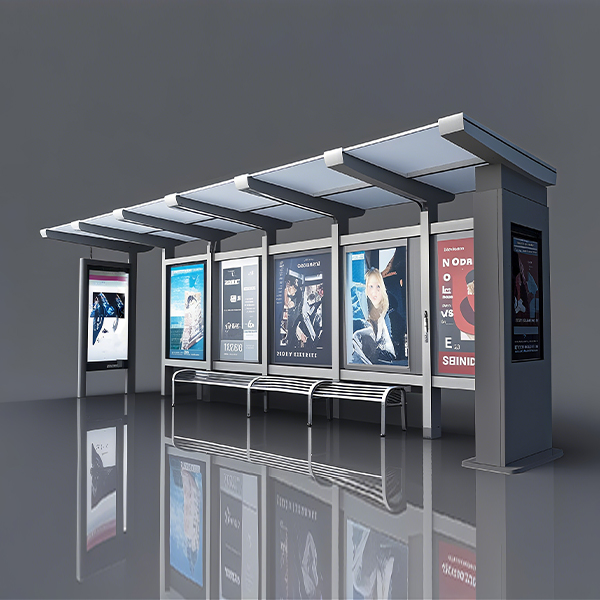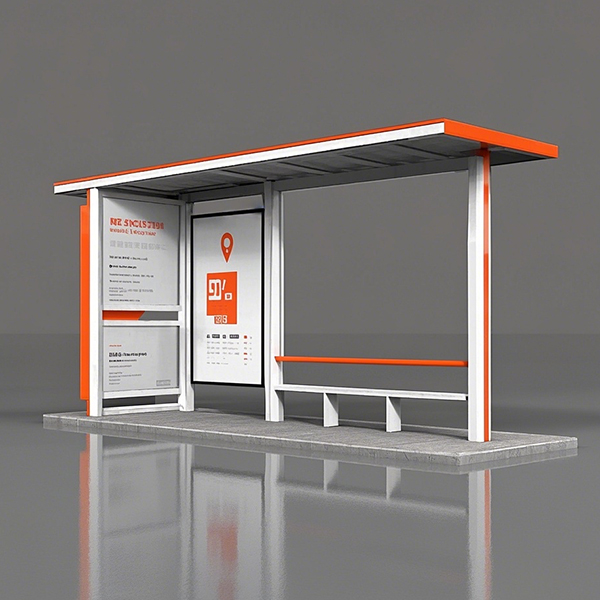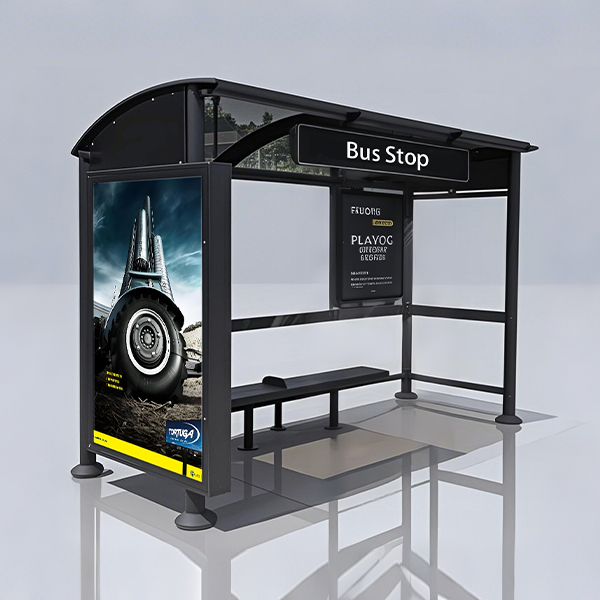
Hospital Bus Shelter
Providing safe and convenient transportation access for patients, visitors, and staff is crucial for any hospital. A well-designed hospital bus shelter plays a significant role in achieving this goal. This guide explores essential aspects of planning, building, and maintaining effective and comfortable shelters for healthcare facilities.
Design Considerations for Hospital Bus Shelters
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Prioritizing accessibility is paramount. Hospital bus shelters must adhere to ADA guidelines, ensuring easy access for wheelchair users, individuals with visual impairments, and other people with disabilities. This includes ramps, appropriate handrails, tactile paving, and clear signage. Consider the shelter's location relative to hospital entrances and parking to minimize distances traveled.
Weather Protection
The shelter should provide adequate protection from the elements. This means a roof that effectively shields from rain, snow, and sun, as well as walls that offer protection from wind and cold. The materials used should be durable and weather-resistant. Consider incorporating features like integrated heating or cooling systems depending on the climate.
Security and Safety
Security is a significant concern. Well-lit shelters, clear visibility from surrounding areas, and potentially security cameras can deter crime. Materials should be chosen for durability and resistance to vandalism. Emergency call buttons or communication systems could also be integrated for added safety.
Comfort and Aesthetics
Comfortable seating, good lighting, and aesthetically pleasing designs can improve the overall patient and visitor experience. Consider using comfortable seating materials and incorporating features like informational displays or digital screens to provide updates on transportation schedules or hospital news.
Construction Materials and Techniques
The choice of materials impacts the shelter's durability, maintenance requirements, and overall cost. Popular options include aluminum, steel, polycarbonate, and composite materials. Each has its advantages and disadvantages concerning strength, weather resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The construction method will depend on the chosen materials and the overall design of the shelter. Proper installation is key to ensure longevity and structural integrity.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance is essential to preserve the hospital bus shelter's functionality and appearance. This includes cleaning, repairing any damage, and ensuring that all features, such as lighting and seating, are functioning correctly. A preventative maintenance schedule can help extend the life of the shelter and minimize costly repairs.
Choosing a Supplier
Selecting a reputable supplier is critical for ensuring quality construction, timely delivery, and ongoing support. Consider factors such as the supplier's experience, reputation, and ability to meet your specific needs. Shandong Luyi Public Facilities Co., Ltd. is a leading provider of high-quality outdoor facilities, including bus shelters designed to meet the needs of healthcare facilities. Their expertise in durable, accessible, and aesthetically pleasing designs makes them a valuable resource for hospitals seeking reliable and effective transportation solutions.
Examples of Successful Hospital Bus Shelter Implementations
Several hospitals have successfully implemented hospital bus shelters that enhance patient and visitor experiences. Researching these case studies can provide valuable insights into best practices and potential solutions for your facility. For detailed information on specific examples, consulting industry publications and hospital websites can be beneficial.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant | Can be more expensive than steel |
| Steel | Strong, relatively inexpensive | Susceptible to rust without proper coating |
| Polycarbonate | Lightweight, impact-resistant, transparent | Can scratch easily |
By carefully considering the design, construction, and maintenance aspects detailed in this guide, hospitals can create hospital bus shelters that are safe, accessible, comfortable, and enhance the overall patient and visitor experience. Remember to prioritize accessibility, weather protection, and security when planning your shelter.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продукты-
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop Shelter
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop Shelter -
 Double Bus Stop Shelter
Double Bus Stop Shelter -
 Stainless Steel Bus Shelter
Stainless Steel Bus Shelter -
 Curved Shed Bus Stop Shelter
Curved Shed Bus Stop Shelter -
 Simple Bus Stop
Simple Bus Stop -
 Rooftop Advertising Bus Stop Shelter
Rooftop Advertising Bus Stop Shelter -
 Large Format Advertising Box Bus Shelter
Large Format Advertising Box Bus Shelter -
 Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter
Three Advertising Box Bus Stop Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter
Semi-enclosed Bus Shelter -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop -
 Semi-enclosed Bus Stop
Semi-enclosed Bus Stop -
 Single Light Box Bus Stop
Single Light Box Bus Stop